Post by geriatrix on Jun 14, 2015 16:31:50 GMT
It is likely that the first musical instrument was the human voice itself, which can make a vast array of sounds, from singing, humming and whistling through to clicking, coughing and yawning. The oldest known Neanderthal hyoid bone with the modern human form has been dated to be 60,000 years old, predating the oldest known Paleolithic bone flute by some 20,000 years, but the true chronology may date back much further.
Most likely, the first rhythm instruments or percussion instruments involved the clapping of hands, stones hit together, or other things that are useful to create rhythm and indeed there are examples of musical instruments which date back as far as the paleolithic, although there is some ambiguity over archaeological finds which can be variously interpreted as either musical or non-musical instruments/tools. Examples of paleolithic objects which are considered unambiguously musical are bone flutes or pipes; paleolithic finds which are open to interpretation are pierced phalanges (usually interpreted as "phalangeal whistles"), objects interpreted as Bullroarers, and rasps.
Music can be thetically traced to prior to the Oldowan era of the Paleolithic age, the anthropological and archaeological designation suggests that music first arose (among humans) when stone tools first began to be used by hominids. The noises produced by work such as pounding seed and roots into meal is a likely source of rhythm created by early humans.
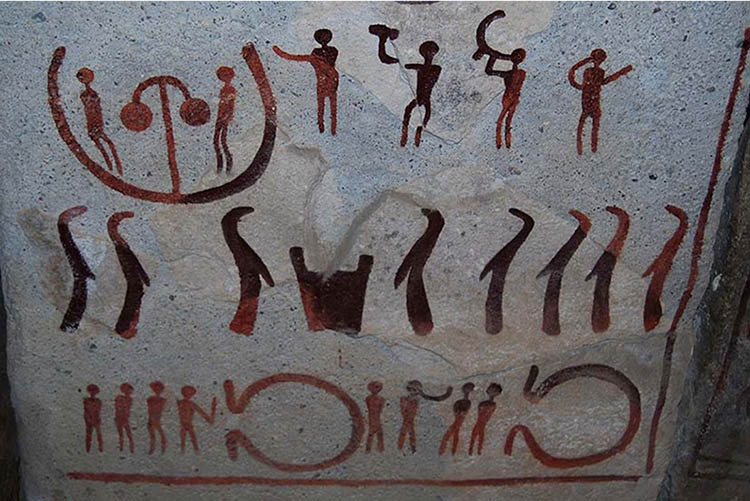

Most likely, the first rhythm instruments or percussion instruments involved the clapping of hands, stones hit together, or other things that are useful to create rhythm and indeed there are examples of musical instruments which date back as far as the paleolithic, although there is some ambiguity over archaeological finds which can be variously interpreted as either musical or non-musical instruments/tools. Examples of paleolithic objects which are considered unambiguously musical are bone flutes or pipes; paleolithic finds which are open to interpretation are pierced phalanges (usually interpreted as "phalangeal whistles"), objects interpreted as Bullroarers, and rasps.
Music can be thetically traced to prior to the Oldowan era of the Paleolithic age, the anthropological and archaeological designation suggests that music first arose (among humans) when stone tools first began to be used by hominids. The noises produced by work such as pounding seed and roots into meal is a likely source of rhythm created by early humans.